The first thing my grandfather said after being freed from captivity was: “Let me see a therapist”. Riddled with trauma sustained from political imprisonment, he entered the UK with no means of income, no resources, and no support. Against the backdrop of global uncertainty, the UK saw a staggering 78,768 asylum applications this year alone (UK Government, 2023). What has changed for the ever-increasing number of people fleeing their country for the promise of a better life?
There is an indisputable increased risk of poorer mental health faced by asylum seekers and refugees (ASR); who consistently experience higher rates of PTSD, depression, and anxiety than the general public (Blackmore et al., 2020). Alongside traumatising life experiences that drive migration (Dowling et al., 2022), arrival to the UK exacerbates anxieties faced through the unique challenges that prevent post-settlement success (Pollard & Howard, 2021).
Despite the growing need, immigration remains a significant factor affecting the underutilisation and experiences of healthcare services (Satinsky et al., 2019). Previous research has identified the barriers faced by ASRs but fails to provide clarity on what is important to ASRs within existing services. Trueba and colleagues (2023) attempted to rectify this by conducting an investigation illuminating the experiences of asylum seekers and refugees, as well as the workers that support them; uniquely contrasting current services available to identify service provision gaps and guide strategies for enhancement.

Asylum seekers and refugees in the UK increasingly face challenges impacting on their experiences of resettlement.
Methods
During this qualitative study, 15 ASRs (asylum seekers and refugees) and support workers from Brighton and Hove, recruited through a combination of purposive and snowballing sampling, were interviewed. Organisations supporting ASRs were also contacted to advertise amongst the participant group.
Of the 9 English-speaking adult ASRs, 67% were male. All had attempted to or used mental health support services and had either achieved refugee status in the past 5 years or currently applying. Of the 6 social workers, the majority were female, and all had worked in either statutory or non-statutory services supporting ASRs in the last 5 years.
Face-to-face semi-structured interviews were conducted in English, using topic guides to centre the conversation on the mental well-being needs of ASR, relevant issues surrounding services provided, and ways to better support ASRs. Thematic analysis was conducted and coded in line with the research aims, before results were relayed back to participants and organisations for feedback.
Results
They identified three themes:
ASR’s (asylum seekers and refugees) need for holistic mental health support
All support workers recognised the need for supporting the complex mental health needs of ASRs, stemming from pre-migratory, migratory, and post-migratory experiences.
Everything in my life worries me… – ASR
Multiple participants recounted the damaging and traumatising effects of the UK asylum-seeking process on mental well-being and “torture” resettlement policy. Key determinants of depressive and stressful feelings were uncertainty, isolation from family and community, precarious living conditions, long waiting times and inability to work.
…whole system… is against refugees… – Support Worker
Support workers felt directing individuals to unknown services may harm well-being; ASR mental health requires specialised, multidimensional attention that is overlooked within generic services. Displaying the need for holistic services that can support the reality of instability faced by ASRs.
The disjunctive between perceived mental health support needs and the available support
The information regarding services in Brighton and Hove consists of an extensive list written in English, of over 100 services, not all of which are ASR/mental health-related or free to access. All ASRs accessed at least one service, however 89% had remaining unpleasant feelings.
Support workers recommended more formal mental health services, whilst ASRs gravitated to those preventing isolation, such as networking events, as well as services addressing the need for language and skill development essential for building new lives in the UK.
…it’s better to support more in the knowledge… ASR
Support workers divulged the inadequacy of the current services, for example limited therapy sessions and lack of interpreters. Services also focus on Western ideas of psychoeducation and life-management techniques, insufficiently supporting disempowered ASRs. However, services opposed adapting due to cost, additional workload, and lack of government pressure.
Barriers to accessing existing mental health support
This theme was further divided into five factors that restrict access to mental health support:
- Complex, unclear, and uncoordinated referral processes
- Communication difficulties
- Stigma, prejudice, and mistrust from both ASR communities and healthcare staff
- Location of services and affordability
- Economic sustainability and support uncertainty
I used to see a her [counsellor]… but now there is no one. – ASR
Across all themes, it was recognised that the UK’s hostile policies are detrimental to the well-being of both ASR and support workers.

Refugees reflected on the importance of integrated support and the multiple barriers that exist in accessing mainstream mental health services.
Conclusions
Overall, the study highlights the intricate mental health challenges faced by ASRs (asylum seekers and refugees). It summarises how the post-migratory phase, influenced by the UK’s hostile asylum policy, contributes to deteriorating mental health. Opposed to the hope of safety, ASRs contend with precarious living conditions, unmet educational needs, poor employment prospects, socio-economic isolation, stigma, and uncertainty. Accessing substantial support proves difficult both for ASR and support workers, discovering healthcare staff denying services that ASR have rights to access. Concluding, there are evident gaps in providing adequate mental health support for ASRs, necessitating holistic, specialised, and sustainable interventions.

Culturally sensitive and accessible interventions may better meet the needs of the asylum seeker and refugee populations in the UK.
Strengths and limitations
Through the qualitative design, the study successfully expands the narrative surrounding the ASR (asylum seekers and refugees) experience, providing raw insight into the challenges faced by ASR communities and support workers, specifically concerning existing regional services. Employing the snowballing technique ensured access to “hard-to-reach” and disenfranchised communities; although lack of representation is a risk, the authors reflect that the participant sample accurately reflected the diaspora present in Brighton and Hove. However, an opposing constraint is that it only garnered participants from Arabic countries, limiting the scope for a UK-wide generalisation by not reflecting all refugee experiences. Although beyond sample bias, it also raises a wider social-political limitation of treatment and support for certain groups of refugees. Public attitudes to those deemed “the right type of refugee”, exhibit a contrast between Ukrainian refugees deemed “so like us” (Newman, 2022) and the mainly Arabic participants in the study. Brighton and Hove alone offers 11 services exclusively for Ukrainian refugees, including mental health and well-being support, business support and even community care like swimming and integration groups (Brighton and Hove City Council, n.d.). This disparity between the care and attitudes afforded to one group over others challenges the belief that services are underfunded or under-researched, but just not available to all.
The generated themes effectively capture participants’ sentiments, yet the first theme may overlook the UK’s policy-active role in hindering comprehensive mental health support and causing re-traumatisation. The significant impact of intentional policies in discouraging people from entering the UK, and fostering a hostile reception, on ASRs should not be downplayed (Kaufman et al., 2022). This is evidenced by the NHS services’ sharing of patient information with the Home Office upon request (Hiam et al., 2018) contributing to the distrust and paranoia experienced by many, highlighting the connection to the UK’s anti-immigration sentiments. This study reveals professionals turning ASRs away from entitled treatment, uncovering an incidence of interpersonal discrimination within healthcare. Unless policies are addressed, holistic mental health support is merely a buzzword. The study failed to include the topic guides that facilitated open conversations, thereby hindering the reader’s ability to discern whether any of the questions were leading.
Concluding, although no participant interested in the study was rejected, the strict inclusion criteria may have deterred those less proficient in English or who have not engaged in services, both key barriers limiting involvement with services and misunderstandings of mental health distress (Paudyal et al., 2021). The provision of interpreters during data collection could have expanded the inclusivity in the sample, making it more representative.

The lack of diversity in the sample imposes further questions on the service engagement and treatment of different refugee communities.
Implications for practice
The study design effectively contrasts perceptions of ASR (asylum seekers and refugees) needs with direct reference to the services available in Brighton and Hove, therefore, replication would be useful in other areas with high ASR populations. It also potentially proves beneficial to different participant groups, for example, children, who face unique and heightened vulnerabilities within the refugee community, leading to elevated rates of PTSD, anxiety, and depression (Dangmann et al., 2022). Ultimately, showcasing the imperative for research that informs services directly.
This study also raised key questions regarding our claimed care for the most vulnerable: Why do entitled individuals face treatment denial by staff? From this discovery, further research can delve into the frequency and impact on future help-seeking. Moreover, broadening research may reveal further patterns of stigma among healthcare staff. Practically, this can then highlight areas to focus practitioner training for staff to understand the complex issues ASRs encounter.
Within policy, this investigation outlines the necessity to alleviate post-migration settlement challenges, reconsider stringent employment and financial aid policies, and reduce application response times that have, at times, spanned decades. Future considerations should review location settlement policies, prioritising effective dispersal planning and preserving family unity. Which could assist in alleviating mental health difficulties compared to those separated from families (Liddell et al., 2021).
Furthermore, support workers expressed the labour in navigating the current services. A practical solution is the implementation of an umbrella agency that provides comprehensible information, assisting in coordinating and guiding requests to support staff that felt overwhelmed and feared recommending unfamiliar services. In line with this, information regarding services should be universally accessible, with broad and accurate translations available for all ASRs seeking care.
The findings call for a shift within current practice, one suggestion being ASRs reclaim their care within social worker roles. The distrust mentioned by numerous participants parallels most refugees’ experiences within their host countries (McGarry, 2018). Western therapeutic ideology’s misalignment with community-centred healing practised elsewhere (Kiselev et al., 2020), highlights services’ need for ASR input within leadership and development, increasing cultural understanding and overcoming barriers to access. This is evident in initiatives like Islington’s Barbers Project, where treatment co-production centres around a sanctuary for the black community (Islington, 2023). My grandad would not have glanced away from his newspaper to entertain the idea of seeking formal help, but found solace and comfort in his community; something our care should emulate.
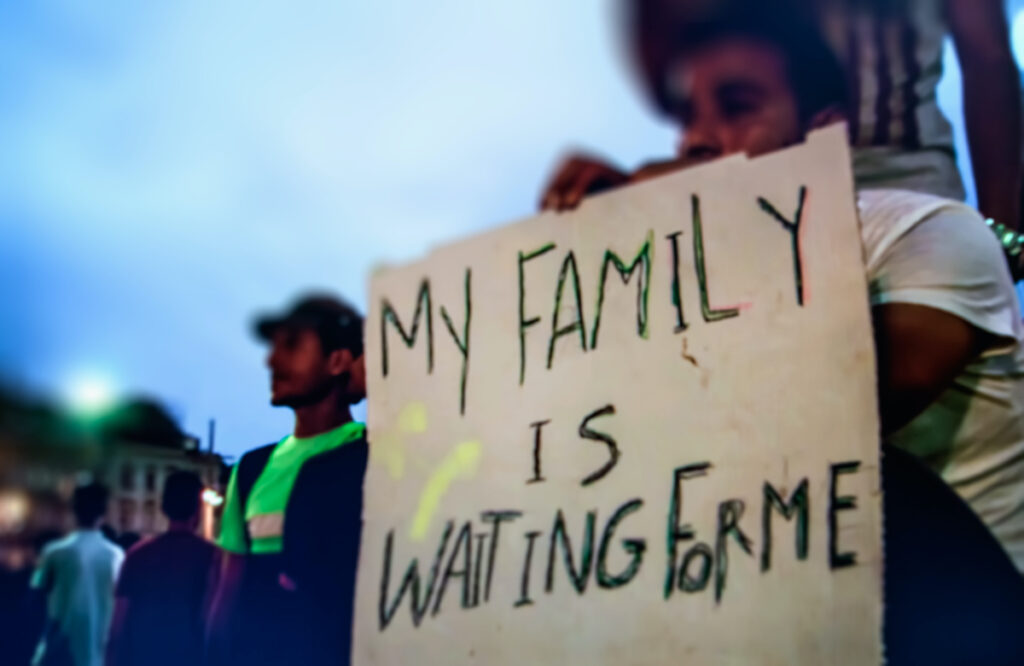
Further consideration needs to be placed in people’s experiences of family separation and strategies supporting family reunification in the UK.
Statements of interest
None.
King’s MSc in Mental Health Studies
This blog has been written by a student on the Mental Health Studies MSc at King’s College London. A full list of blogs by King’s MSc students from can be found here, and you can follow the Mental Health Studies MSc team on Twitter.
We regularly publish blogs written by individual students or groups of students studying at universities that subscribe to the National Elf Service. Contact us if you’d like to find out more about how this could work for your university.
Links
Primary Paper
Trueba, M. L., Axelrod, T., & Ayeb-Karlsson, S. (2023). Are asylum seekers and refugees provided with appropriate mental health support in the United Kingdom? Journal of Ethnic and Migration Studies, 49(13), 3163-3183. https://doi.org/10.1080/1369183x.2023.2181126
Other References
Blackmore, R., Boyle, J. A., Fazel, M., Ranasinha, S., Gray, K. M., Fitzgerald, G., Misso, M., & Gibson-Helm, M. (2020). The prevalence of mental illness in refugees and asylum seekers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Med,17(9), e1003337. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1003337
Brighton and Hove City Council. (n.d.). Support services for Ukrainian refugees in Brighton & Hove. www.brighton-Hove.gov.uk. Retrieved December 3, 2023, from https://www.brighton-hove.gov.uk/supporting-ukrainian-humanitarian-crisis/support-services-ukrainian-refugees-brighton-hove
Dangmann, C., Dybdahl, R., & Solberg, O. (2022). Mental health in refugee children. Curr Opin Psychol, 48, 101460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2022.101460
Dowling, A., Kunin, M., & Russell, G. (2022). The impact of migration upon the perceived health of adult refugees resettling in Australia: a phenomenological study. Journal of Ethnic and Migration Studies, 48(7), 1536-1553. https://doi.org/10.1080/1369183X.2020.1771173
GOV.UK. (2023, August 4). How many people do we grant protection to? GOV.UK. Retrieved Novermeber 26, 2023, from https://www.gov.uk/government/statistics/immigration-system-statistics-year-ending-march-2023/how-many-people-do-we-grant-protection-to#asylum-applications
Hiam, L., Steele, S., & McKee, M. (2018). Creating a ‘hostile environment for migrants’: the British government’s use of health service data to restrict immigration is a very bad idea. Health Econ Policy Law, 13(2), 107-117. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1744133117000251
Islington. (2023, January 20). Young Black Men and Mental Health Programme | Islington Council. www.islington.gov.uk. Retrieved November 26, 2023, from https://www.islington.gov.uk/social-care-and-health/health-services-in-islington/mental-health/young-black-men-and–mental-health-programme
Kaufman, K. R., Bhui, K., & Katona, C. (2022). Mental health responses in countries hosting refugees from Ukraine. BJPsych Open, 8(3), 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjo.2022.55
Kiselev, N., Pfaltz, M., Haas, F., Schick, M., Kappen, M., Sijbrandij, M., De Graaff, A. M., Bird, M., Hansen, P., Ventevogel, P., Fuhr, D. C., Schnyder, U., & Morina, N. (2020). Structural and socio-cultural barriers to accessing mental healthcare among Syrian refugees and asylum seekers in Switzerland. Eur J Psychotraumatol, 11(1), 1717825. https://doi.org/10.1080/20008198.2020.1717825
Liddell, B. J., Byrow, Y., O’Donnell, M., Mau, V., Batch, N., McMahon, T., Bryant, R., & Nickerson, A. (2021). Mechanisms underlying the mental health impact of family separation on resettled refugees. Australian & New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry, 55(7), 699-710. https://doi.org/10.1177/0004867420967427
McGarry, O. (2018). What strategies to address communication barriers for refugees and migrants in health care settings have been implemented and evaluated across the WHO European Region? NCBI Bookshelf. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534365/
Newman, D. (2022, March 2). “The Right Kind of Refugees”: Racism in the Western media coverage of the conflict in Ukraine. Media Diversity Institute. Retrieved December 1, 2023, from https://www.media-diversity.org/the-right-kind-of-refugees-racism-in-the-western-media-coverage-of-the-conflict-in-ukraine/
Paudyal, P., Tattan, M., & Cooper, M. J. F. (2021). Qualitative study on mental health and well-being of Syrian refugees and their coping mechanisms towards integration in the UK. BMJ Open, 11(8), e046065. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2020-046065
Pollard, T., & Howard, N. (2021). Mental healthcare for asylum-seekers and refugees residing in the United Kingdom: a scoping review of policies, barriers, and enablers. Int J Ment Health Syst, 15(1), 60. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13033-021-00473-z
Satinsky, E., Fuhr, D. C., Woodward, A., Sondorp, E., & Roberts, B. (2019). Mental health care utilisation and access among refugees and asylum seekers in Europe: A systematic review. Health Policy, 123(9), 851-863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healthpol.2019.02.007







