Exposure to bright light synchronizes the central circadian clock in our brain, whereas proper meal timing helps sync the timing of different clock genes throughout the rest of our body.
One of the most important breakthroughs in recent years has been the discovery of “peripheral clocks.” We’ve known for decades about the central clock—the so-called suprachiasmatic nucleus. It sits in the middle of our brain right above the place where our optic nerves cross, allowing it to respond to day and night. Now we also know there are semi-autonomous clocks in nearly every organ of our body. Our heart runs on a clock, our lungs run on one, and so do our kidneys, for instance. In fact, up to 80 percent of the genes in our liver are expressed in a circadian rhythm.
Our entire digestive tract is, too. The rate at which our stomach empties, the secretion of digestive enzymes, and the expression of transporters in our intestinal lining for absorbing sugar and fat all cycle around the clock. So, too, does the ability of our body fat to sop up extra calories. The way we know these cycles are driven by local clocks, rather than being controlled by our brain, is that you can take surgical biopsies of fat, put them in a petri dish, and watch them continue to rhythm away.
All of this clock talk is not just biological curiosity. Our health may depend on keeping all of them in sync. “Imagine a child playing on a swing.” Picture yourself pushing, but you become distracted by what’s going on around you in the playground and stop paying attention to the timing of the push. So, you forget to push or you push too early or too late. What happens? Out of sync, the swinging becomes erratic, slows, or even stops. That is what happens when we travel across multiple time zones or have to work the night shift.
The “pusher” in this case is the light cues falling onto our eyes. Our circadian rhythm is meant to get a “push” from bright light every morning at dawn, but if the sun rises at a different time or we’re exposed to bright light in the middle of the night, this can push our cycle out of sync and leave us feeling out of sorts. That’s an example of a mismatch between the external environment and our central clock. Problems can also arise from a misalignment between the central clock in our brain and all the other organ clocks throughout our body. An extreme illustration of this is a remarkable set of experiments suggesting that even our poop can get jet lag.
As you can see below and at 2:31 in my video How to Sync Your Central Circadian Clock to Your Peripheral Clocks, our microbiome seems to have its own circadian rhythm.
Even though the bacteria are down where the sun doesn’t shine, there’s a daily oscillation in both bacterial abundance and activity in our colon, as you can see in the graph below and at 2:43 in my video. Interesting, but who cares? We all should.
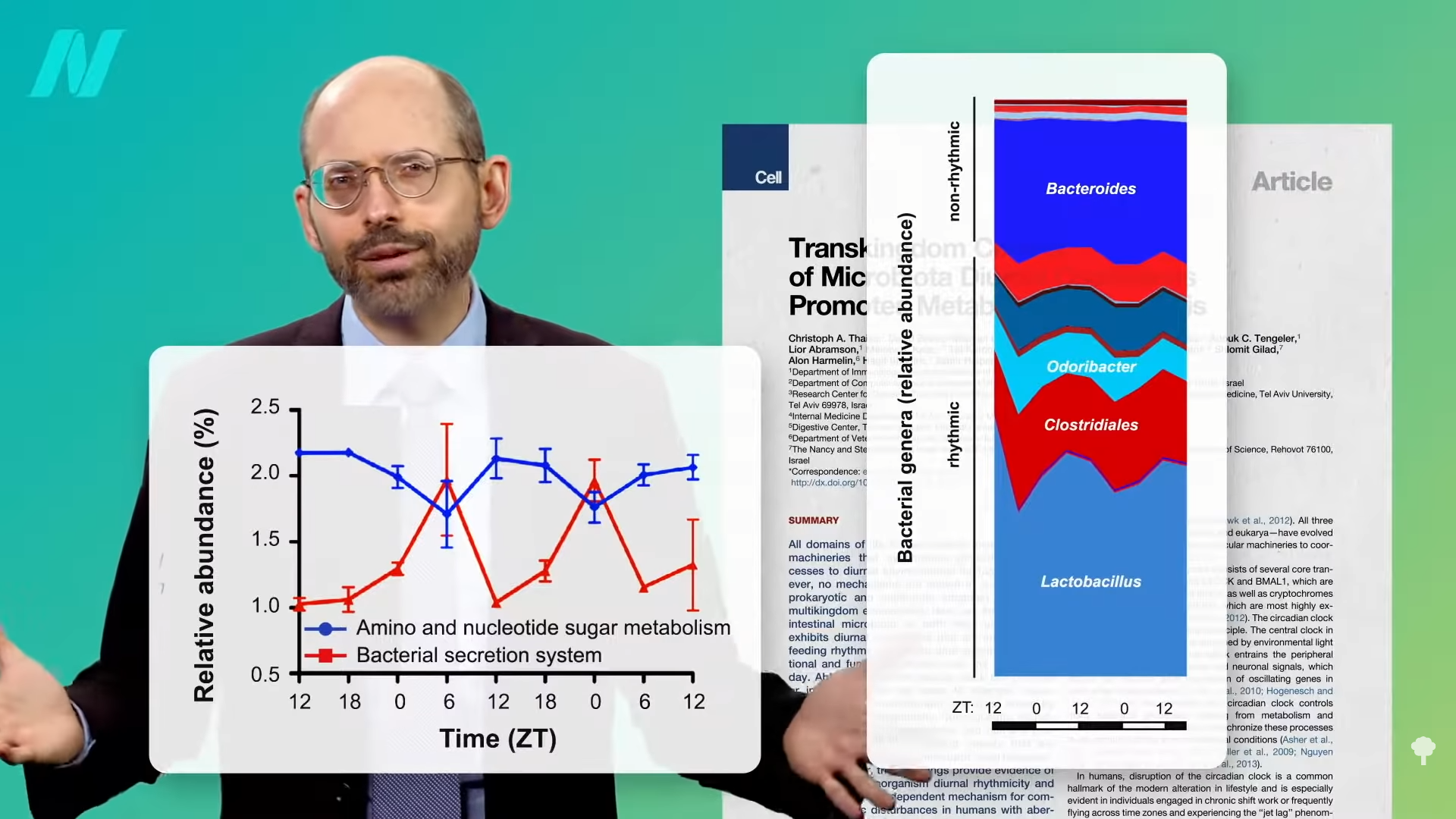
Check this out: If you put people on a plane and fly them halfway around the world, then feed their poop to mice, those mice grow fatter than mice fed preflight feces. The researchers suggest the fattening flora was a consequence of “circadian misalignment.” Indeed, several lines of evidence now implicate “chronodisruption”—the state in which our central and peripheral clocks diverge out of sync—as playing a role in conditions such as premature aging and cancer, as well as ranging to others like mood disorders and obesity.
Exposure to bright light is the synchronizing swing pusher for our central clock. What drives our internal organ clocks that aren’t exposed to daylight? Food intake. That’s why the timing of our meals may be so important. Researchers removed all external timing cues by keeping study participants under constant dim light and found that you could effectively decouple central rhythms from peripheral ones just by shifting meal times. They took blood draws every hour and biopsies of the subjects’ fat every six hours to demonstrate the resulting metabolic disarray.
Just as morning light can help sync the central clock in our brain, morning meals can help sync our peripheral clocks throughout the rest of our body. Skipping breakfast disrupts the normal expression and rhythm of these clock genes themselves, which coincides with adverse metabolic effects. Thankfully, they can be reversed. Take a group of habitual breakfast-skippers and have them eat three meals at 8:00 am, 1:00 pm, and 6:00 pm, and their cholesterol and triglycerides improve, compared to taking meals five hours later at 1:00 pm, 6:00 pm, and 11:00 pm. There is a circadian rhythm to cholesterol synthesis in the body, too, which is also “strongly influenced by food intake.” This is evidenced by the 95 percent drop in cholesterol production in response to a single day of fasting. That’s why a shift in meal timing of just a few hours can result in a 20-point drop in LDL cholesterol, thanks to eating earlier meals, as you can see below and at 5:00 in my video.

If light exposure and meal timing help keep everything synced, what happens when our circumstances prevent us from sticking to a normal daytime cycle? We’ll find out in The Metabolic Harms of Night Shifts and Irregular Meals. If you’re just coming into the series, be sure to check out the related posts below.







