Are the apparent adverse effects of heavy cannabis use on the bone just due to users being thinner?
It’s been recognized for decades that cigarette smoking can have “a major effect” on bone health, “increasing the lifetime risk of hip fracture by about half.” It also appears to impair bone healing, so much so that surgeons ask if they should discriminate against smokers because their bone and wound-healing complication rates are so high. What about smoking marijuana?
As I discuss in my video Effects of Marijuana on Weight Gain and Bone Density, “There is accumulating evidence to suggest that cannabinoids [cannabis compounds] and their receptors play important roles in bone metabolism by regulating bone mass, bone loss, and bone cell function.” Okay, but are they “friend or foe?”
“Results from research on cannabinoids and bone mineral density in rodent models have been inconsistent. Some studies show increased bone formation, others have demonstrated accelerated bone loss, and yet others have shown no association. This variation in results may be due [in part] to differences in the mouse strain, sex, age…” If you can’t even extrapolate from one mouse to another, how can you extrapolate from mice to human beings?
What if you just measure cannabis use and bone mineral density in people? Researchers tested thousands of adults and asked them about their cannabis use. There did not appear to be any link between the two, which is a relief. However, in this study, “heavy” cannabis use was defined as just five or more days of use in the previous 30 days. The researchers didn’t ask beyond that, so, theoretically, someone who smoked just five joints in their entire life could be categorized as a “heavy user” if they happened to use it five times in the last four weeks.
How about cannabis use on 5,000 separate occasions over a lifetime? Now that’s a heavy user—decades of regular use. In that case, heavy use was “associated with low bone mineral density and an increased risk of fractures”—about double the fracture rate presumably due to lower bone density in the hip and spine, although heavy cannabis users were also thinner on average, and thinner people have lighter bones.
Hip fracture risk goes down as our weight goes up. Nearly half of underweight women have osteoporosis, but less than 1 percent of obese women do, which makes total sense. Being obese forces our body to make our bones stronger to carry around all of that extra weight. That’s why weight-bearing exercise is so important to constantly put stress on our skeleton. When it comes to our bones, it’s use it or lose it. That’s why astronauts can lose a percent of their bone mass every month in “long-duration spaceflight.” Their bodies aren’t stupid. Why waste all that energy making a strong skeleton if you aren’t going to put any weight on it?
So, maybe the reason heavy cannabis users have frailer bones is because they tend to be about 15 pounds lighter. Wait a second. Marijuana users are slimmer? What about the munchies? “The lower BMI that was observed in heavy cannabis users at first sight seems counterintuitive,” given marijuana’s appetite stimulation, but this isn’t the first time this has been noted.
“Popular culture commonly depicts marijuana users as a sluggish, lethargic, and unproductive subculture of compulsive snackers,” and marijuana has indeed been found to increase food intake. A single hit can increase appetite, so you’d expect obesity rates to rise in states that legalized it. But, if anything, the rise in obesity appeared to slow after medical marijuana laws were passed, whereas it appeared to just keep rising in other states, as you can see in the graph below and at 3:45 in my video.
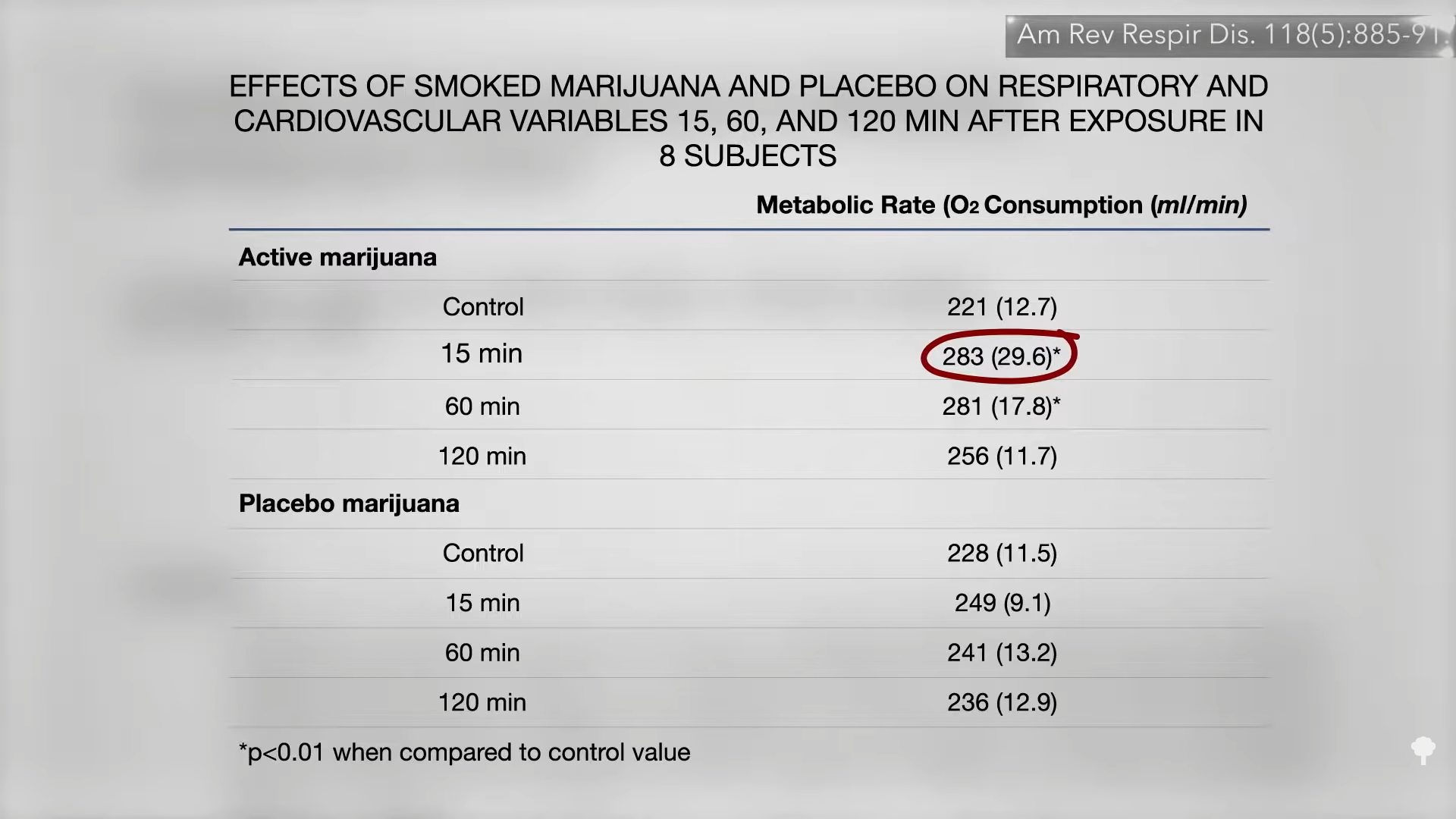
The reason pot smokers may be slimmer is because of the effect of smoked marijuana on metabolism. We’ve known for more than nearly 40 years that within 15 minutes of lighting up, our metabolic rate goes up by about 25 percent and stays there for at least an hour, as you can see below and at 4:04 in my video. So, that may be playing a role.
Is that why heavy cannabis use is associated with lower bone mineral density and increased risk of fractures? Because users just aren’t as overweight? No. Even when taking BMI into account, heavy cannabis use appears to be “an independent predictor” of weaker bones.
I originally released a series of marijuana videos in a webinar and downloadable digital DVD. There are still a few videos coming out over the next year, but if you missed any of the already published ones, see the related posts below.
For more on bone health, check out the related posts below.







