How may we preserve bone and mass on a low-calorie diet?
One of the most consistent benefits of calorie restriction is that blood pressure improves in as little as one or two weeks. Blood pressure may even be normalized in a matter of weeks and blood pressure pills discontinued. Unfortunately, this can work a little too well and cause orthostatic intolerance, which can manifest as lightheadedness or dizziness upon standing and, in severe cases, may cause fainting, though staying hydrated can help.
What about loss of muscle mass? In the CALERIE trial, which I profile in my video Potential Pitfalls of Calorie Restriction, 70 percent of the body weight the subjects lost was fat and 30 percent was lean body mass. So, they ended up with an improved body composition of about 72 percent lean mass compared to 66 percent in the control group, as you can see at 0:51 in my video. And, even though leg muscle mass and strength declined in absolute terms, relative to their new body size, they generally got stronger.
Is there any way to preserve even more lean mass, particularly among older individuals who naturally tend to lose muscle mass with age? Increased protein intakes are commonly suggested, but most studies fail to find a beneficial effect on preserving muscle strength or function whether you’re young or old, active or sedentary. For example, during a 25 percent calorie restriction, researchers randomized overweight older men and women to either a normal-protein diet with 4 grams for every ten pounds of body weight or a high-protein diet with about 8 grams per ten pounds. That doubling of protein intake had no discernible effect on lean body mass, muscle strength, or physical performance. As you can see below and at 1:48 in my video, most such studies found the same lack of benefit, but when they’re all put together, one can tease out a small advantage of about one or two pounds of lean mass over an average of six months. 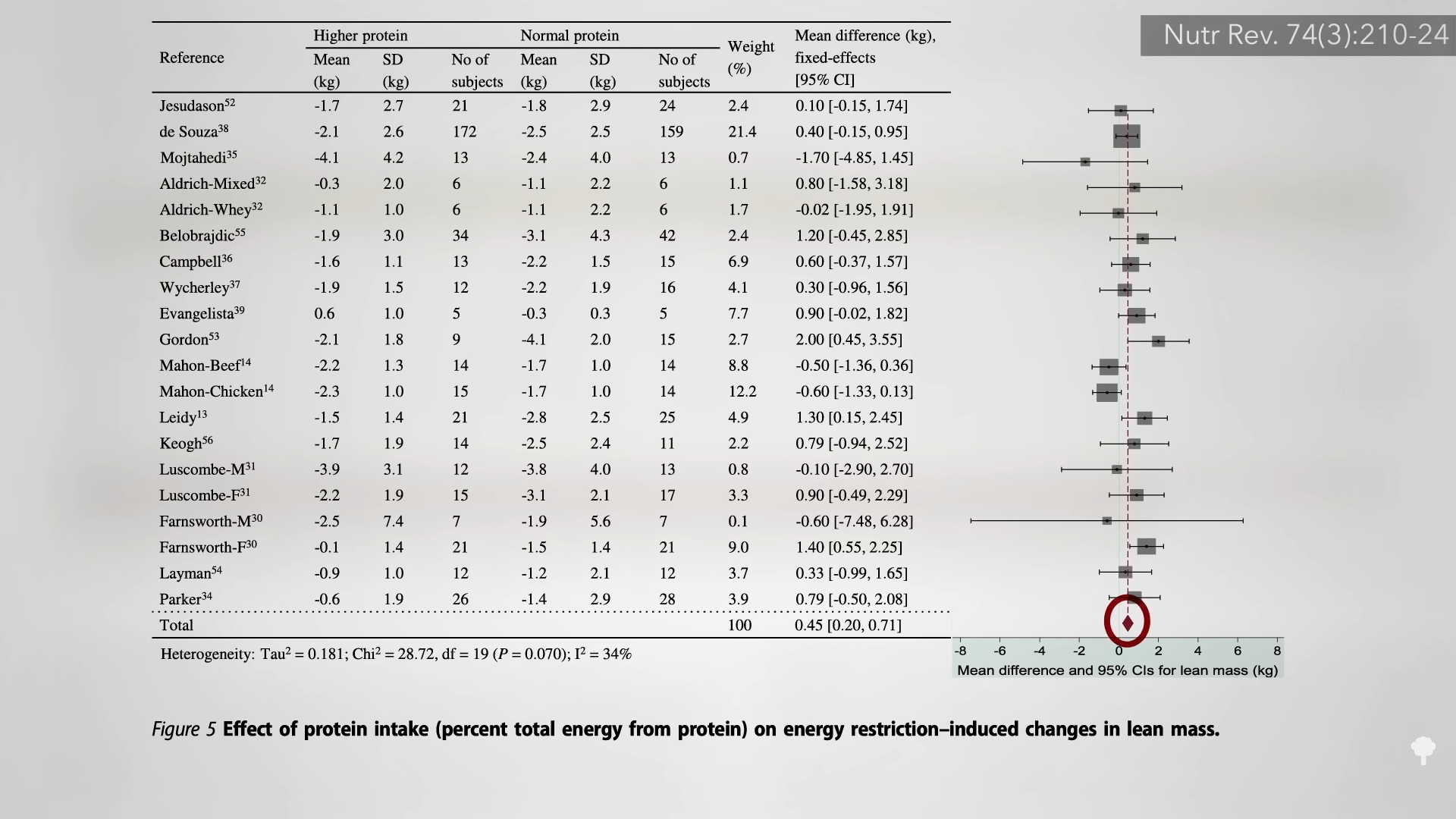
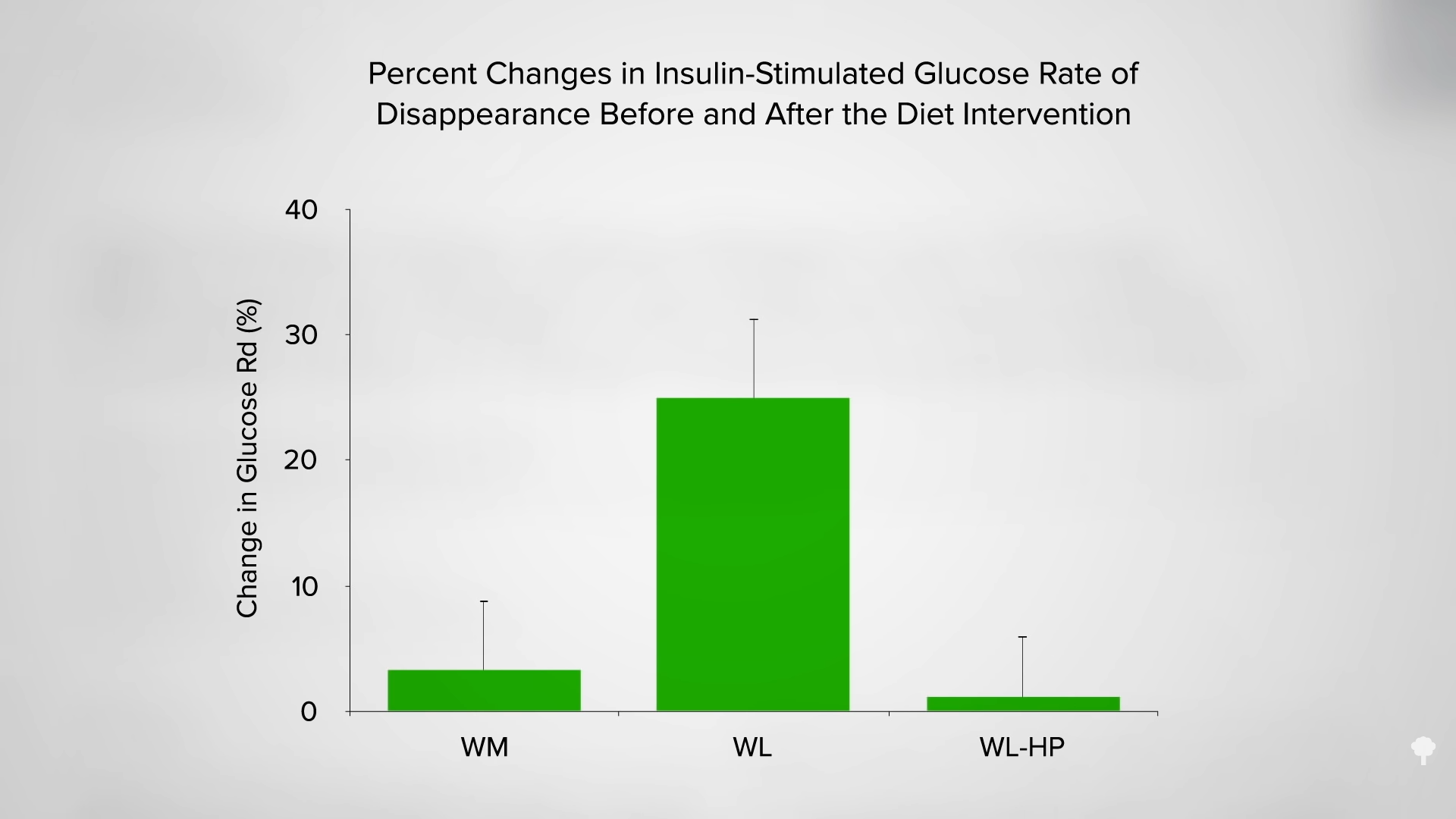
Unfortunately, high protein intake during weight loss has also been found to have “profound” negative metabolic effects, including undermining the benefits of weight loss on insulin sensitivity. As you can see in the graph below and at 2:14 in my video, if you lose 20 pounds, you can dramatically improve your body’s ability to handle blood sugars, compared to subjects in a control group who maintained their weight. But, if you lose the exact same amount of weight on a high-protein diet, getting about an extra 30 grams a day, it’s like you never lost any weight at all.
Though you can always bulk back up after weight loss, the best way to preserve muscle mass during weight loss is to exercise. The CALERIE study had no structured exercise component, and, similar to bariatric surgery, about 30 percent of the weight loss was lean mass. In contrast, that proportion was only about 16 percent of The Biggest Loser contestants, chalked up to their “vigorous exercise program.” Resistance training even just three times a week can prevent more than 90 percent of lean body mass loss during calorie restriction.
The same may be true of bone loss. Lose weight through calorie restriction alone, and you experience a decline in bone mineral density in fracture risk sites, such as the hip and spine. In the same study, though, those randomized to lose weight with exercise did not suffer any bone loss. The researchers concluded: “Our results suggest that regular EX [exercise] should be included as part of a comprehensive weight loss program to offset the adverse effects of CR [caloric restriction] on bone.”
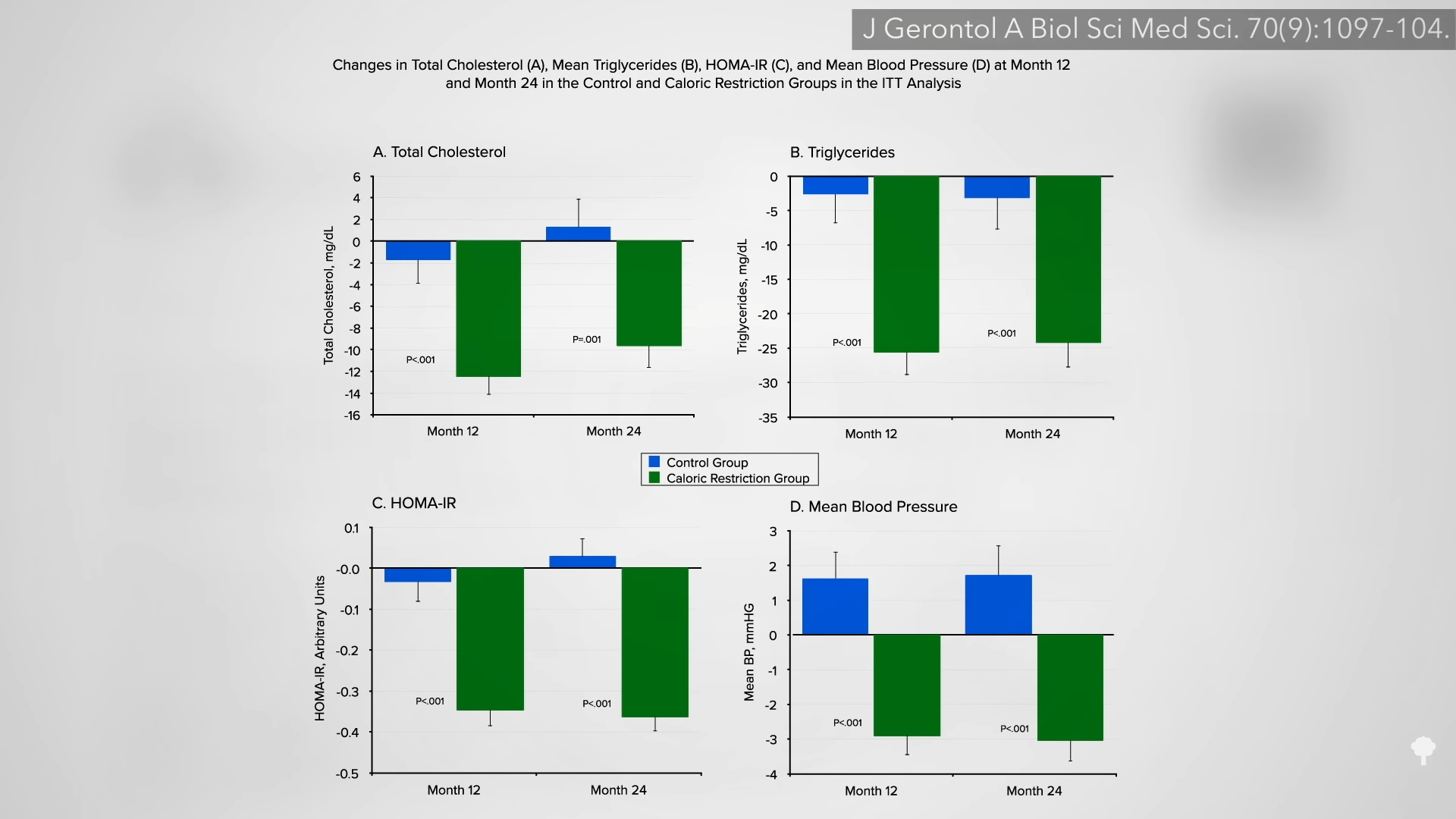
It’s hard to argue with calls for increased physical activity, but even without an exercise regimen, the “very small” drop in bone mineral density in the CALERIE trial might only increase a ten-year risk of osteoporotic fracture by about 0.2 percent. The benefits of calorie restriction revealed by the study included improvements in blood pressure and cholesterol, as you can see in the graph below and at 3:54 in my video, as well as improved mood, libido, and sleep. These would seem to far outweigh any potential risks. The fact that a reduction in calories seemed to have such wide-ranging benefits on quality of life led commentators in the AMA’s internal medicine journal to write: “The findings of this well-designed study suggest that intake of excess calories is not only a burden to our physical homeostasis [or equilibrium], but also on our psychological well-being.”
Check out my other videos on calorie restriction, fasting, intermittent fasting, and time-restricted eating in the related videos below.







